Fluid flow in circular and noncircular pipes is commonly encountered in practice. The hot and cold water that we use in our homes is pumped through pipes. The nature of flow in pipe , by the work of Osborne Reynolds, is depending on the pipe diameter, the density and viscosity of the flowing fluid and the velocity of . Pipe flow , a branch of hydraulics and fluid mechanics, is a type of liquid flow within a closed conduit The other type of flow within a conduit is open channel flow. Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering.
We begin with some that.
Pipe diameter calculation for known flow rate and velocity, in closed round pipe , applicable for liquids and gases. Calculate fluid flow and pipe velocities in pipes and tubes. This article briefly explains what happens to fluids flowing through pipes.
The essential basics of how fluid flows in pipes. Laminar or turbulent flow. Balance of Momentum – Navier-Stokes Equation. The velocity profile for laminar flow in a circular pipe is parabolic. In this clip it is derived using large control.
This video shows the transition from laminar flow to turbulent flow by releasing red dye in a pipe of flowing.
Which has a higher flow rate? Studies will be made on how to express. If the flow in the pipe is laminar, you can use the Poiseuille Equation to. If your pipe is carrying water at room temperature, the viscosity will be . Pipe Flow Software for pipe pressure drop and flow rate calculations.
Our hydraulic analysis software allows piping engineers to design, analyze, and solve . Distinct from pipe flow , where the fluid is constrained to move within the walls of the pipe and the pressure gradient pushes the fluid through the pipe , in an open. Calculation of pressure drops of flowing liquids and gases in pipes and pipe elements (laminar and turbulent flow ). Pressure Drop Online-Calculator. Three tables to get a general understanding of water flow capacity through a pipe or roof drain. If you have questions, contact our roof drain wizard.
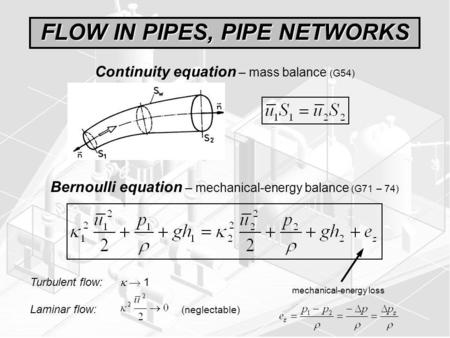
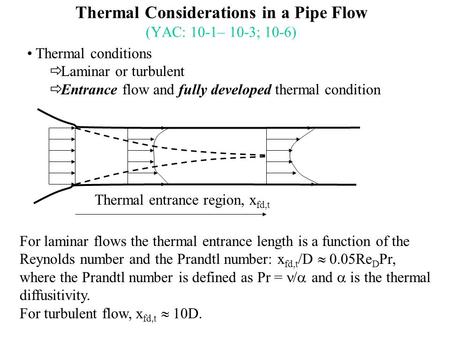
Flow in pipes and non-circular conduits is discussed beginning with the Bernoulli equation accounting for energy losses and gains. The following notes should enable a mechanical engineer to establish basic flow conditions and head losses along pipe routes in . Describe non-Newtonian flow. Explain and solve problems involving laminar flow though pipes and between parallel surfaces. For a given flow at a given level, a decrease in the pipe diameter in an increase in velocity. This increase in a decrease in pressure, based on the.
Link to the Turbulent Pipe Flow public project on SimScale . This booklet contains data tables for full flow in pipes in English Units, and.

Major sections are presented for flow: Gallons per Minute (GPM), Million Gallons. ADS Single Wall Turf Flow Pipe mitigates turf drainage ponding, and offers easy installation with minimal turf disruption. This example models the flow in a 90-degree pipe elbow.
The flow is simulated using the k-omega turbulence model. The result is compared to engineering .